316 stainless steel tubing is widely used across industries where corrosion resistance, strength, and reliability are essential. Its molybdenum content enhances resistance to chlorides and harsh environments, making it suitable for demanding operational conditions. Understanding where this material is commonly applied helps engineers and buyers match performance requirements to real-world use. Continue reading “8 Typical Industrial Applications of 316 Stainless Tubing [Infographic]”
9 Must-Know Facts About 309 Stainless Steel Pipe & Tube [Infographic]
Stainless steel plays an essential role in high-temperature and corrosive environments, and the 309 grade is one of the most widely used options in industrial applications. It delivers excellent strength and durability even under continuous heat exposure. These features make it suitable for demanding uses across refineries, power plants, chemical industries, and heavy fabrication. Continue reading “9 Must-Know Facts About 309 Stainless Steel Pipe & Tube [Infographic]”

The Engineering Strength Behind 316 Stainless Steel Tube: What Makes It Superior?

Industrial environments demand the use of materials that won’t fail when conditions turn harsh. The 316 grade stainless steel tube has earned its reputation in sectors where corrosion resistance matters most. From chemical processing to marine applications, this grade proves its worth on a daily basis. Continue reading “The Engineering Strength Behind 316 Stainless Steel Tube: What Makes It Superior?”

What Makes a 316 Seamless Tube Ideal for High-Purity and Sanitary Applications?

When material selection directly impacts product safety and regulatory compliance, choosing the wrong tubing can lead to contamination, costly recalls, and production shutdowns. A 316 grade seamless tube provides the specific properties needed in industries handling sensitive fluids or gases without compromising purity or introducing unwanted particles into processes.
Continue reading “What Makes a 316 Seamless Tube Ideal for High-Purity and Sanitary Applications?”

Precision, Performance, and Power: The Role of Light Wall Stainless Steel Tubing in Modern Engineering

Modern engineering systems demand that they be made from materials that deliver exceptional performance under challenging conditions. Light wall stainless steel tubing has emerged as a critical component across industries requiring precise fluid control, thermal management, and structural integrity. The selection of appropriate tubing directly influences system efficiency, operational costs, and long-term reliability in demanding industrial environments.
Engineers and procurement professionals recognize that light wall stainless steel tubing offers distinct advantages in applications where weight reduction and material efficiency matter. The thinner wall construction maintains structural performance while reducing overall system mass and material costs. This balance between strength and efficiency makes such tubing particularly valuable in sectors where space constraints and weight considerations affect design decisions and operational outcomes. Continue reading “Precision, Performance, and Power: The Role of Light Wall Stainless Steel Tubing in Modern Engineering”
7 Engineering Facts About 4130 Rectangular Tubing You Should Know [Infographic]

Known for its exceptional combination of strength, toughness, and machinability, 4130 rectangular tubing is a trusted choice across aerospace, automotive, and structural engineering industries. This alloy, composed mainly of chromium and molybdenum, offers a unique balance of durability and light weight that makes it suitable for high-stress environments where precision and performance are critical. Continue reading “7 Engineering Facts About 4130 Rectangular Tubing You Should Know [Infographic]”

From Refineries to Power Plants: How Arch City Steel & Alloy Pipes Support Heavy Industry
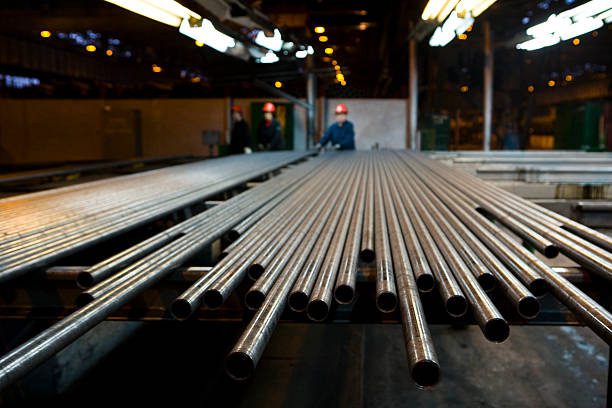

From Refineries to Power Plants: How Arch City Steel & Alloy Pipes Support Heavy Industry
- Heavy industry operations demand piping systems that can withstand extreme conditions without failure. Refineries and power plants operate under constant thermal stress, corrosive environments, and high-pressure scenarios that test material limits daily. Arch City Steel & Alloy understands that selecting the right pipe grade determines whether a facility runs smoothly or faces costly shutdowns and safety risks.
- Arch City Steel & Alloy provides industrial-grade piping solutions engineered for demanding applications across energy sectors. The company supplies specific alloy grades designed to handle temperature fluctuations, pressure variations, and chemical exposure common in refinery and power generation environments. Material selection directly impacts operational reliability and maintenance costs over a facility’s lifespan.

8 Industrial Uses of 304H Stainless Steel [Infographic]

304H stainless steel is a specialized high-carbon version of the widely used 304 grade, designed to deliver superior performance in high-temperature environments. Its higher carbon content provides greater strength at elevated temperatures, making it an ideal material for demanding applications where both durability and resilience are essential. Continue reading “8 Industrial Uses of 304H Stainless Steel [Infographic]”

Why Trusted 4130 Chromoly Tubing Suppliers Are Vital for Aerospace and Motorsport Industries

Aerospace and motorsport industries operate under extreme conditions where material failure is not an option. Components in these sectors face intense mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, and constant vibration during operation. Choosing reliable 4130 grade chromoly tubing suppliers ensures access to materials that meet the demanding performance standards required in high-stakes applications. Continue reading “Why Trusted 4130 Chromoly Tubing Suppliers Are Vital for Aerospace and Motorsport Industries”
Why Engineers Choose Experienced 4130 Tubing Suppliers

Engineering projects demand materials that perform under extreme conditions without failure. When specifying chromoly tubing for aerospace, automotive, or industrial applications, the supplier relationship often determines project success. Experienced 4130 grade tubing suppliers provide more than just material—they deliver technical expertise, verified certifications, and consistent quality that prevent costly delays and rework. Continue reading “Why Engineers Choose Experienced 4130 Tubing Suppliers”
